Dependence of rate on reactant concentrations
Dependence of rate on reactant concentrations: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Rate Law Expression of a Chemical Reaction,Rate Constant of a Chemical Reaction,Units of Rate Constant etc.
Important Questions on Dependence of rate on reactant concentrations
The sum of the powers of the concentration terms in the experimentally determined rate equation is known as:
A first order reaction is complete in minute. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to be complete:
,
The rate constant for the reaction, is . If the rate is , then the concentration of is
In a first-order reaction, the concentration of reactant decreases from in. The rate constant of reaction in is
Consider a reaction . When concentration of both the reactants G and H is doubled, the rate increases by eight times. However, when concentration of G is doubled keeping the concentration of H constant, the rate is doubled. The overall order of the reaction is:
Consider a reaction . When concentration of both the reactants and is doubled, the rate increases by eight times. However, when the concentration of is doubled, keeping the concentration of constant, the rate is doubled. The overall order of the reaction is:
Consider the chemical reaction:
The rate of this reaction can be expressed in terms of time derivatives of concentration of Identify the correct relationship amongst the rate expressions:
What is the principle behind Ostwald's isolation method?
For a zero-order reaction, with the initial reactant concentration , the time for completion of the reaction is:
Which of the following is incorrect?
The reaction between and follows the equation . The following data were observed:
| Initial rate of appearance of | ||
The value of the rate constant for the given reaction is:
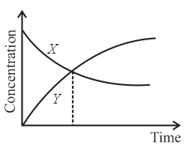
The accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species and for the elementary reaction as a function of time. The point of intersection of two curves represents:
The order of a reaction for which a linear line (with a negative slope) is obtained in a graph of vs is:
Two-third life for a first-order reaction is minutes. The value of its velocity constant is nearly
The reaction, follows the first order kinetics, the rate law being . However the reaction shows that, it is second order. Explain.
Consider a reaction that is first order in both directions
Initially only is present, and its concentration is Assume and are the concentrations of at time and at equilibrium, respectively. The time at which is:
For a first order reaction , the rate constant is . If the initial concentration of is , the concentration of at any time is given by the expression:
For a given reaction the rate of reaction can be represented by
For the following elementary reaction, determine its order of reaction and the dimensions of the rate constant:
The time taken for the completion of three-fourths of a first-order reaction is
